Data organisation
The “runPL_*.py” scripts are designed to run sequentially, each handling a specific stage of data reduction, calibration, and analysis.
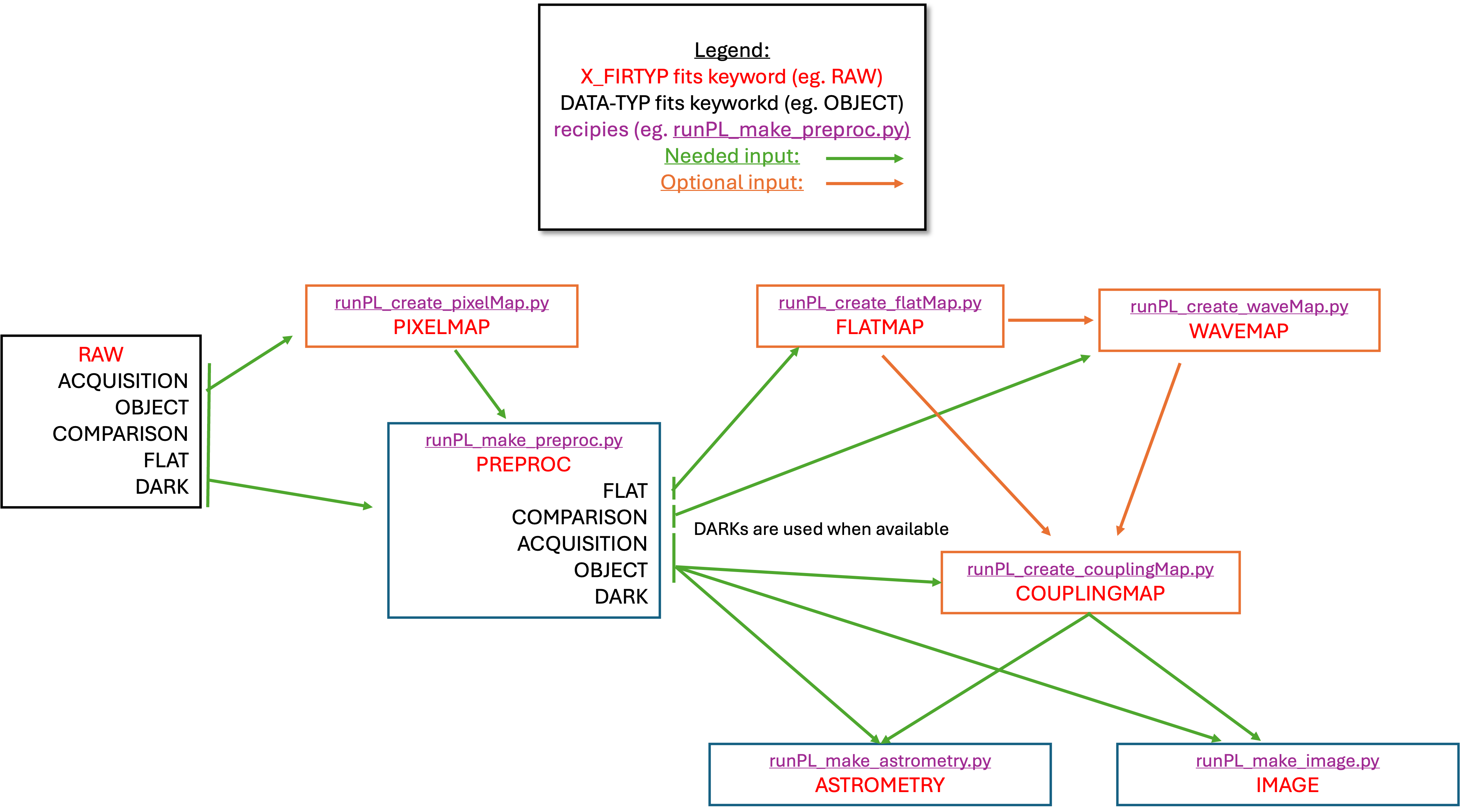
Two main FITS file keywords are used to organise the data: “DATA-TYP” and “X_FIRTYP”. The first keyword is specific to SUBARU, the second one is specific to the FIRST instrument.
The user will give the files as arguments to each script. If no argument is given, the script will look for all files within the current directory. The script will automatically select relevant data based on the FITS keywords.
Installation
There are two ways to install and use the FIRST Pipeline:
Option 1: Development Installation (Recommended)
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/scexao-org/first_pipeline.git cd first_pipeline
Install the package in development mode:
pip install -e .
Install ESO FITS Tools (required for
runPL_dfits):# On macOS with Homebrew: brew install cfitsio # Or install from source: # See: https://github.com/granttremblay/eso_fits_tools
Option 2: Using Scripts Directly
If you prefer to run scripts directly without package installation:
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/scexao-org/first_pipeline.git cd first_pipeline
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run scripts from the first_pipeline directory:
# Run from the first_pipeline/ directory python runPL_changeKeyword.py [options] [files...] python runPL_create_pixelMap.py [options] [files...] # etc.
Note:
Option 1 allows you to run commands from anywhere as
runPL_changeKeyword,runPL_create_pixelMap, etc.Option 2 requires you to be in the
first_pipeline/directory and usepython script_name.py
Pipeline Structure
Directory Organization
first_pipeline/
├── __init__.py # Package initialization
├── setup.py # Package setup and installation
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
├── classes/ # Data structure classes
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── runPL_class_couplingMap.py
│ ├── runPL_class_dataCube.py
│ ├── runPL_class_pixelMap.py
│ └── runPL_class_flatMap.py
├── libraries/ # Utility functions
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── runPL_library_basic.py
│ ├── runPL_library_io.py
│ ├── runPL_library_linalg.py
│ └── runPL_library_plots.py
├── [main scripts] # Primary pipeline scripts
├── runPL_create_pixelMap.py
├── runPL_make_preproc.py
├── runPL_create_flatMap.py
├── runPL_create_waveMap.py
├── runPL_create_couplingMap.py
├── runPL_make_image.py
└── runPL_make_astrometry.py
Workflow
Inspect FITS files:
./runPL_dfits <file>Update keywords if needed:
python runPL_changeKeyword.py --X_FIRTYP=RAW *.fitsCreate pixel map:
python runPL_create_pixelMap.py --filter_files *.fitsPreprocess data:
python runPL_make_preproc.py /data/directoryCreate flat field map:
python runPL_create_flatMap.py *.fitsGenerate wavelength map:
python runPL_create_waveMap.py *.fitsCreate coupling maps:
python runPL_create_couplingMap.py *.fitsPerform astrometry if needed:
python runPL_make_astrometry.py *.fitsReconstruct images if needed:
python runPL_make_image.py *.fits
Key Components
Shell and Python scripts: Each major step is a separate script
Data flow: Raw FITS files → Pixel Map → Preprocessing → Wavelength Map → Coupling Maps → Calibration → Image Reconstruction
Script chaining: Output from one script is often input for the next
Modern CLI: All scripts use
argparsefor professional command-line interfaces
Requirements
Python dependencies:
Core scientific stack:
numpy,scipy,matplotlibAstronomy libraries:
astropy,astroplanUtility libraries:
tqdm(progress bars)
External tools:
dfitsfrom ESO FITS Tools for FITS inspectionFITS keywords: Scripts rely on specific header keywords for file selection